SAP BASIS and Security Authorization
SAP Plant Maintenance
A D V E R T I S E M E N T
Security Components
IDES � the �International Demonstration
and Education System� in the R/3 System,
represents a model company. It consists of an international group with
subsidiaries in several countries. IDES contains application data that can be
used to portray numerous business scenarios in the R/3 System. The business
processes in the IDES system are designed to reflect real-life business
requirements, and have access to many realistic characteristics. IDES uses
easy-to-follow business scenarios to show you the comprehensive functions of the
R/3 System. The focal point of IDES, however, is not the functionality itself,
but the business processes and their integration.
These IDES business processes are described in detail within
this online documentation. The individual demos provide you with an overview of
the sample data, and contain step-by-step instructions of how to execute the
individual processes.
IDES not only covers the Logistics area, but also Financials,
and Human Resources. It demonstrates how the R/3 System is able to support
practically all types of industries, from discrete production through to process
industries, from engineering-to-order to repetitive manufacturing. However, IDES
is not a sector-oriented model company. The individual processes are based on
practice-oriented data for sectors such as Retailing or Aerospace and Defense.
The IDES group manufactures products as diverse as elevators, motorcycles, and
paints.
IDES is managed by SAP just as any regular business
enterprise. SAP regularly updates the IDES data (master data, transaction data,
and customizing). We also carry out period-end closing and plan with different
time-horizons. Transaction data are generated to ensure that the information
systems in all areas have access to realistic evaluation data. We are constantly
implementing new, interesting business scenarios to highlight the very latest
functions available in the R/3 System. New functions, such as internet
technology, are represented and documented by IDES scenarios.
Above all, IDES demonstrates the incredible potential of the
integrated applications within the R/3 System. We cover all aspects of a
business enterprise, including human resources, financial accounting, product
cost planning, overhead management, profitability analysis, planning, sales and
distribution, materials management, production, and much, much more. We have
also integrated document administration and third-party CAD systems within the
IDES system. This means that you can call up and display external documents, or
access CAD drawings.
IDES shows you how the R/3 System supports production
processes, the supply chain, and the efficient usage of global resources. Or
perhaps you would like to increase your understanding of just-in-time-production
or the integration of the electronic KANBAN system in an MRP II environment?
IDES provides the ideal way to learn about areas such as Product Cost
Controlling, Activity-Based Costing, or integrated Service Management and Plant
Maintenance. How to manage high inflation is just one of the ever-growing number
of IDES business scenarios that you can choose from.
SAP Authorization Concept
The SAP authorization concept is based upon the logical
relationship between a user ID and the range of system authorizations with which
it can be associated. The architecture of the authorization system is based upon
the utilization of several individuals but related logical components: Profiles,
Objects, Fields, and Authorizations. The user ID refers exclusively to profiles.
Each profile grants a set of specific system access authorizations to user.
Figure 2 illustrates the hierarchical authorization concept in SAP.
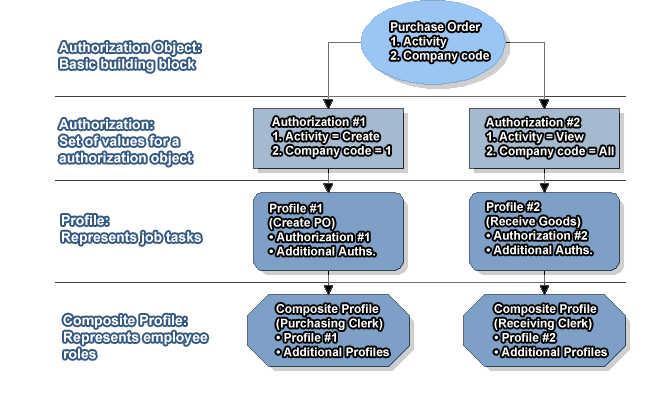
Figure 2
Composite Profiles
Composite profiles refer to the various employee roles
available in the corporation (for instance: Purchasing / Receiving Clerk or
Accounts Agent). As the name suggests, composite profiles may contain multiple
user IDs necessary to perform all the business operations associated with a
particular role. A composite profile may encapsulate another composite profile(s).
In practice, a model composite profile should be recognized for each possible
role in the organization, which may be used to produce hybrid composite
profiles. The over-existence of the hybrids can defy the very purpose of
composite profiles and they should be created only when specific needs arise.
User Ids
User ids allow access to SAP applications. Each user must
have a corresponding profile specifically assigned. In many situations, multiple
composite profiles can be assigned to a user ID, depending on the role(s) an
individual user is responsible for, in the business processes.
Authorizations
Authorizations are the key building blocks of SAP security.
Authorization is the process of assigning values to fields present in
authorization objects. In SAP, access to all system functionality is achieved
through a complex array of authorizations. Sometimes users find that they lack
the necessary authorizations to perform a certain function in the system, in
which case the message: �You are not authorized�� is displayed at the bottom of
the screen.
An authorization process may ask for second associated authorization process
which in turn asks for third and so on. For example, the task of paying a vendor
invoice may require 10 different authorizations.
Security Configuration in SAP
Security configuration and administration in SAP is a
multi-phase process. Four key security components are required to ensure the
adequate security, privacy, and integrity of information. The phases are as
follows:
1. User Authentication
The first phase comprises confirmation of user identity and
results in authentication of user. Unauthorized access to SAP system is
prevented through this initial check. This ensures system integrity by
regulating secure access through genuine user authentication.
2 Creating and Assigning Authorization Profiles
A Profile Generator (PG) is used to automatically generate
and assign authorization profiles. This tool was released with SAP version 3.1g
and above. The administrator can also create authorization profiles manually.
Note: Profile Generator can be retroactively
installed in SAP versions 3.0f and above.
The authorization objects can be selected using the SAP
Profile Generator. Administrators can automatically generate authorization
profiles for function-specific access to SAP users after configuring initial
settings.
The entire authorization functionality of SAP signifies a new
approach to authorization. The administrator can define user authorization based
on SAP functions. Based on the selected function, the PG groups objects in
administrator-created authorization profiles.
Authorization profiles created by a Profile Generator are
based on the given authorizations. It also speeds up the process and simplifies
administrator/user communication facilitating both the administrator and users
to use the same SAP function terminology. To auto-generate an Authorization
profile, an Activity Group needs to be created.
Activity Groups contain simple profiles and usually represent
employee or job roles. They are user-defined and allow administrator to organize
and maintain system activities. Activity group when used as an information
database reduces data entry time. Administrators can define activity groups in
two steps:
- Selecting the criteria, such as access controls.
- Dividing the activities into appropriate groups.
For example, activities can be organized by functions, such
as human resources, payroll, or administration or by job classes, such as
computer programming activities, or accounting activities. A combination of
function-specific activity and job-specific activity can also be implemented.
Security implementation with the new Profile Generator is
based on the creation of activity groups or a collection of linked or associated
activities, such as tasks, reports, and transactions.
Consider a business situation involving a company, ABC Inc.
faced with transaction security hiccups in business dealings with its dealers.
To address this problem, the company can create authorization profiles for its
dealers using the profile generator features. This can be done by implementing
the following instruction set:
-
Instruction 1: A dealer activity group should be created.
Name this activity group as Dealer.
-
Instruction 2: All dealer-specific business transactions
should be included in the activity group.
-
Instruction 3: Generate an authorization profile for
Dealers.
-
Instruction 4: Assign Dealer to a �new user� or in your
system and update master records.
Following this procedure will ensure complete functional access to the new
user using the system as Dealer.
Auditing and Monitoring
In this subsequent phase, a track of the authorizations
created (previous phase) is kept. Detailed accounts of system events are used to
record the actions of a user corresponding to that unique user account
identifier. Auditing/Monitoring activities should be in compliance with
enterprise�s overall IT strategy and should be performed on a weekly, monthly,
quarterly, and yearly basis.
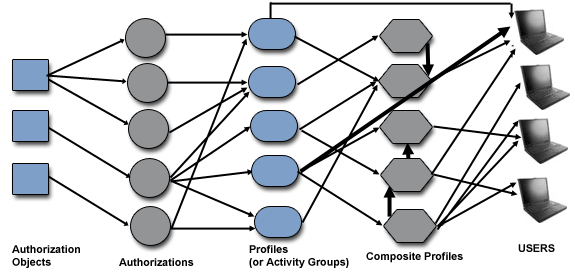
Figure 3
There are some key tasks that should be included in a
monitoring plan. The following reviews should be a part of an ideal monitoring
plans.
Using System Logs and Security Audit Logs
The system log records critical information important events.
Each individual application server maintains local log files to which the
information is written periodically. The security audit log records areas such
as successful and unsuccessful dialog log-on attempts, RFC log-on attempts,
changes to user master records, and transaction starts.
Reviewing User Activity
All SAP system users must be continuously monitored so that their problems can
be rectified as soon as they occur. The timely attention to user problems can
reduce administration overheads.
For example, if a SAP administrator wants to check for
unrecognizable user Ids or the users trying to use non-permitted transactions,
administrator can execute transaction AL08 and review user activity.
Monitoring User access in BASIS User Group
The BASIS users in a SAP system have access to sensitive
areas of an organization. Therefore it is vital to monitor their access.
Following instructions can be performed to check the access of BASIS User group.
Instruction Set
- Enter transaction SUIM to view Repository Information of the system.
- Follow the Menu Path:
- User > Lists of users (according to selection criteria) >
user IDS (Double Click).
Monitoring Change Requests
All change requests need to be properly reviewed and
controlled prior to being applied. This formal process needs to be detailed
enough to ensure that separation of duties and other control features are not
breached. Strong integration knowledge of the SAP system is required for this
review. Critical profiles, authorizations, and transactions need to be
identified and treated even more carefully.
Checking Important Default SAP Profiles
Administrators must check that default profiles act a
template for user defined profiles and are not directly used in production.
Default profiles contain values, which apply to all application servers. These
include: SAP_ALL, SAP_NEW, S_A.ADMIN, S_A.CUSTOMIZ, S_A.DEVELOP, S_A.DOKU,
S_A.SYSTEM, S_A.USER, S_ENT_IMG_GE, S_WF_ALL, and P_ALL.
Changing Default SAP User ID�s
SAP comes with some pre-configure clients (independent business units). They
are client 000, 001 and 066 in the non-IDES system. In the IDES system, client
800 is the default client. SAP installation process automatically creates
default user Ids and their corresponding passwords. SAP administrators must
ensure that they are not used to access the system. The following table explains
default user Ids in various SAP clients.
| User
Ids |
Client
Name |
User
Function |
|
SAP* |
000 and 001 |
SAP* denotes the default
super user and has all administrative powers. |
|
DDIC |
000 and 001 |
DDIC user is responsible
for the maintenance of the ABAP/4 Dictionary and the software logistics. |
|
EarlyWatch |
066 |
The EarlyWatch user has
access only to monitoring and performance data. |
Instruction Set
- Change all default passwords and verifying the password change by
logging into various client areas.
- Assign SAP* to the Super user group.
- Enter transaction SE16.
- Enter SAP* into the field called BNAME.
- Click �Execute� and verify.
- As a final step, check that the secret super user has been created (with
a different user ID and password). All of the authorizations assigned to
SAP* should then be removed (an empty profile list followed by a password
change.
|
