MIDI Basics
The Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) protocol provides a standardized
and efficient means of conveying musical performance information as electronic
data. MIDI information is transmitted in "MIDI messages", which can be thought
of as instructions which tell a music synthesizer how to play a piece of music.
A D V E R T I S E M E N T
The synthesizer receiving the MIDI data must generate the actual sounds. The
MIDI 1.0 Detailed Specification provides a complete description of the MIDI
protocol.
The MIDI data stream is a unidirectional asynchronous bit stream at 31.25
Kbits/sec. with 10 bits transmitted per byte (a start bit, 8 data bits, and one
stop bit). The MIDI interface on a MIDI instrument will generally include three
different MIDI connectors, labeled IN, OUT, and THRU. The MIDI data stream is
usually originated by a MIDI controller, such as a musical instrument keyboard,
or by a MIDI sequencer. A MIDI controller is a device which is played as an
instrument, and it translates the performance into a MIDI data stream in real
time (as it is played). A MIDI sequencer is a device which allows MIDI data
sequences to be captured, stored, edited, combined, and replayed. The MIDI data
output from a MIDI controller or sequencer is transmitted via the devices' MIDI
OUT connector.
The recipient of this MIDI data stream is commonly a MIDI sound generator or
sound module, which will receive MIDI messages at its MIDI IN connector, and
respond to these messages by playing sounds. Figure 1 shows a simple MIDI
system, consisting of a MIDI keyboard controller and a MIDI sound module. Note
that many MIDI keyboard instruments include both the keyboard controller and the
MIDI sound module functions within the same unit. In these units, there is an
internal link between the keyboard and the sound module which may be enabled or
disabled by setting the "local control" function of the instrument to ON or OFF
respectively.
The single physical MIDI Channel is divided into 16 logical channels by the
inclusion of a 4 bit Channel number within many of the MIDI messages. A musical
instrument keyboard can generally be set to transmit on any one of the sixteen
MIDI channels. A MIDI sound source, or sound module, can be set to receive on
specific MIDI Channel(s). In the system depicted in Figure 1, the sound module
would have to be set to receive the Channel which the keyboard controller is
transmitting on in order to play sounds.
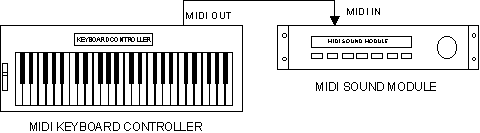
Figure 1: A Simple MIDI System
Information received on the MIDI IN connector of a MIDI device is transmitted
back out (repeated) at the devices' MIDI THRU connector. Several MIDI sound
modules can be daisy-chained by connecting the THRU output of one device to the
IN connector of the next device downstream in the chain.
Figure 2 shows a more elaborate MIDI system. In this case, a MIDI keyboard
controller is used as an input device to a MIDI sequencer, and there are several
sound modules connected to the sequencer's MIDI OUT port. A composer might
utilize a system like this to write a piece of music consisting of several
different parts, where each part is written for a different instrument. The
composer would play the individual parts on the keyboard one at a time, and
these individual parts would be captured by the sequencer. The sequencer would
then play the parts back together through the sound modules. Each part would be
played on a different MIDI Channel, and the sound modules would be set to
receive different channels. For example, Sound module number 1 might be set to
play the part received on Channel 1 using a piano sound, while module 2 plays
the information received on Channel 5 using an acoustic bass sound, and the drum
machine plays the percussion part received on MIDI Channel 10.
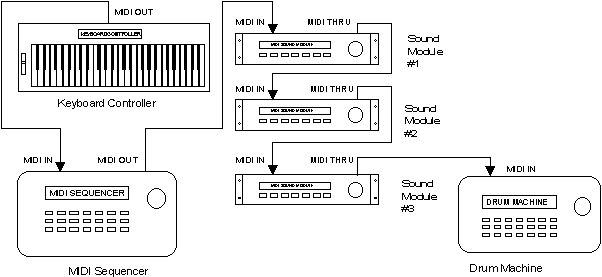
Figure 2: An Expanded MIDI System
In this example, a different sound module is used to play each part. However,
sound modules which are "multitimbral" are capable of playing several different
parts simultaneously. A single multitimbral sound module might be configured to
receive the piano part on Channel 1, the bass part on Channel 5, and the drum
part on Channel 10, and would play all three parts simultaneously.
Figure 3 depicts a PC-based MIDI system. In this system, the PC is equipped
with an internal MIDI interface card which sends MIDI data to an external
multitimbral MIDI synthesizer module. Application software, such as Multimedia
presentation packages, educational software, or games, sends MIDI data to the
MIDI interface card in parallel form over the PC bus. The MIDI interface
converts this information into serial MIDI data which is sent to the sound
module. Since this is a multitimbral module, it can play many different musical
parts, such as piano, bass and drums, at the same time. Sophisticated MIDI
sequencer software packages are also available for the PC. With this software
running on the PC, a user could connect a MIDI keyboard controller to the MIDI
IN port of the MIDI interface card, and have the same music composition
capabilities discussed in the last two paragraphs.
There are a number of different configurations of PC-based MIDI systems
possible. For instance, the MIDI interface and the MIDI sound module might be
combined on the PC add-in card. In fact, the Multimedia PC (MPC) Specification
requires that all MPC systems include a music synthesizer, and the synthesizer
is normally included on the audio adapter card (the "sound card") along with the
MIDI interface function. Until recently, most PC sound cards included FM
synthesizers with limited capabilities and marginal sound quality. With these
systems, an external wavetable synthesizer module might be added to get better
sound quality. Recently, more advanced sound cards have been appearing which
include high quality wavetable music synthesizers on-board, or as a
daughter-card options. With the increasing use of the MIDI protocol in PC
applications, this trend is sure to continue.
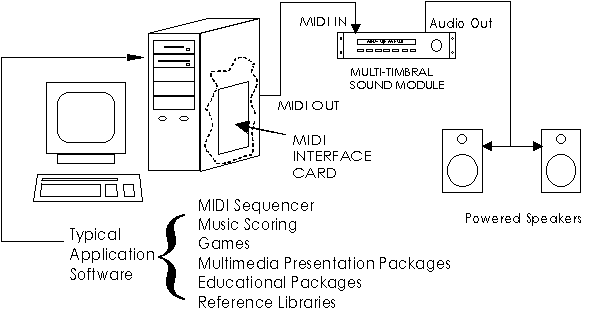
Figure 3: A PC-Based MIDI System
|
