Data Warehousing Design Methodologies
Data warehousing is more an art-form than cookie cutter science. The business variables and technical risks are very unique to each installation. The business users have different goals and expectations. Data warehousing is more often successful than not if there is a reservoir of data warehousing expertise in-house.
A D V E R T I S E M E N T
The two major design methodologies of data warehousing are from Ralph Kimball and Bill Inmon. The design methodologies developed by Kimball and Inmon have lines drawn in the sand. Quite often the design chosen will be a combination of the methodologies below and additional requirements - the data warehouse design third way.
 Kimball's Data Warehousing Design Methodology
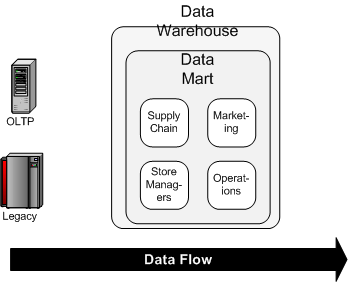
Kimball's Data Warehousing Design Methodology
Kimball views data warehousing as a constituency of data marts. Data marts are focused on delivering business objectives for departments in the organization. And the data warehouse is a conformed dimension of the data marts. Hence a unified view of the enterprise can be obtain from the dimension modeling on a local departmental level.
 Inmon's Data Warehouse Design Methodology
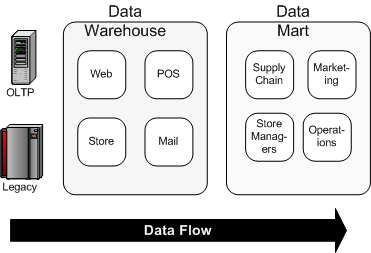
Inmon's Data Warehouse Design Methodology
Inmon beliefs in creating a data warehouse on a subject-by-subject area basis. Hence the development of the data warehouse can start with data from the online store. Other subject areas can be added to the data warehouse as their needs arise. Point-of-sale (POS) data can be added later if management decides it is necessary.The data mart is the creation of a data warehouse's subject area.
Over time it has become apparent to proponents of bottom-up and top-down data warehouse design that both methodologies have benefits and risks. Hybrid methodologies have evolved to take advantage of the fast turn-around time of bottom-up design and the enterprise-wide data consistency of top-down design. And there are third ways that can be unique to an enterprise's needs.
|
