Managing Files and Projects
A D V E R T I S E M E N T
Deleting a Class
Now that you know how to create a
project and a Java class, you'll need to know how to delete them. To remove a
class file from a project, right click on it in the package explorer and select
"Delete". A dialog box asking you to confirm will appear. Selecting yes will
delete the Java file. Removing a Java file from a Project using this method
will delete the Java file from disk. In other words, once you select
"Delete", the file will be gone for good, and there is no Undo option on the
Eclipse menu to undelete the file.
Deleting a Project
Deleting a project is safer.
Right click on the project in the package viewer. Again, select "Delete" from
the context menu. This time, a dialog box will appear asking you if you want to
also delete all of the files in the project's directory. The default is "Do not
delete contents". If you select this option, the Java files that were a part of
that project will not be deleted. If you are sure you no longer need the
project delete the contents instead.
Importing Files
File System Import
The contents of a Java project
are defined by the contents of the folder in your filesystem in which the
project is stored. What happens if you want to grab a Java file from some other
location and make it part of your current project? This process is called
importing and can be done simply with Eclipse: simply right click on the
Project in the package explorer and select "Import". This will bring up an
Import window that has a couple of options to choose. The two relevant ones are
"File System" and "Zip File". If you choose "File System", you can import any
Java file from anywhere else on your local file system (i.e., your computer). So
you could use this option to pull in a Java file from a directory other than the
one you're using for your current Java project. This can be accomplished by
first selecting the directory from which you want to import the Java files by
either filling in the edit box at the top of the Import window or by selecting
it with the "Browse" button. After doing so, you'll see the directory appear in
the window on the left. Next to the folder name you'll see a square box that you
can check and uncheck. Checking the box means "import everything in that
directory". When you click on the directory name, the right window will display
all of the files in that directory. Each file will have a similiar checkbox.
Each file that is checked will be imported into your project. Importing
files into your project will cause copies to be created of the files you're
importing. Thus, once your import a file, a copy of that file will be
created and put in your project's directory. Changing the file you've imported
will not change the original source file, and vice versa. Deleting a file you've
imported from your project will not delete the original file.
Zip
(jar) File Import
If you want to import a jar file,
you'll want to select your project, right click and choose "Import", but instead
choose "Zip file". The options here are very similiar to when importing from the
file system, since a Zip/Jar is really a miniature file system stored in a
single file. After you choose the Jar file you want to import from, you'll see a
directory structure with checkboxes that behaves just like when importing from
the file system. Check the folders or individual files you want to import and
select "Finish." Again, copies of the contents of the Jar file are made, so you
can safely manipulate the files and delete them without affecting the source Jar
file.
Exporting Files
This time, we're going to be
creating a copy of our project somewhere else. Right click on the project and
select "Export". You'll see a list of options similiar to the list for importing
files, and again the relevant options are "File System" and "JAR file". This
time, the left and right windows show you the contents of your current project.
Checking and unchecking items here selects which files in your project you want
to export. If you choose "File System", you simply specify the folder where you
want to copy your project files and hit "Finish".
Creating a Jar File
Creating a JAR file is slightly
more complicated. JAR files can contain either compiled code, source code, or
both. By default, Eclipse assumes you're exporting compiled code, so it only
lists .class files and other files required by the compiled code. To
change this, modify the checkboxes right below the folder/file windows so that
"Export generated class files and resources" is unchecked and "Export java
source files and resources" is checked. If you are submitting a project via a
JAR file and you forget to do this, you will not provide your .java files.
Make sure you export your Java source files if what you want to provide is your
source code. Once that is straightened out, choose a location for your JAR
file and then hit "Finish". You can test whether or not your JAR file worked by
creating a new Project and importing your JAR file into that new project as
described above. If the new project you created looks just like your original
project, chances are your export worked correctly.
Displaying Line Numbers in the Editor
You'll probably find it useful to
display line numbers in your code editor. When an error occurs in your code, the
Java VM will tell you what line number in the source code it occurred on. You
can find that line quickly if your line numbers are displayed. In order to do
this, select Window -> Preferences on the main menu, which will bring up the
Eclipse options, where you can set your preferences (things like font
size/color, etc). On the left there is a list of categories. Click the '+' next
to "Java" to expand that category, and select "Editor". The right window will be
populated with a group of tab panes. You want to select the "Appearance" tab (it
is selected by default). Check the second checkbox ("Show line numbers") and hit
"OK". You should see line numbers appear in your editor (if you have a Java file
open).
Renaming Projects, Classes, Files and Variables
To change the name of a project,
class, file, variable or method highlight the item and select
"Refractor"->"Rename". You will then be prompted to enter a new name. Hit "OK"
and you are done.
Searching in a Java File
IIf you are editing a Java file
and you want to locate a specific phrase somewhere in your code, you can use
Eclipse's search tool. Eclipse has a more advanced searching mechanism than most
Windows applications. Select Search -> Search. This will bring up the search
window, which has a series of tabs. To use a standard phrase-based search,
select the first tab and enter a search string, and hit search. The search
results will be displayed at the bottom of the screen. Double clicking on the
results listed will focus the editor on that instance of the search string.
These searching utilities makes it easy to quickly locate anything in your
project, so experiment with the search tool -- it can save you a lot of time
later.
Interactions Pane
The interactions pane is part of
the Dr. Java perspective and appears as a tab pane along with "Console". The
interactions pane is basically a command interpreter that feeds Java code into a
running JVM, which means you can use it to test a statement, or series of
statements, in Java code. The Dr. Java perspective allows you to practice
different constructs of the language without having to write a full class. For
example, if you want to verify how perform String manipulation in Java, you
could write the following statements in the Interactions Pane which will process
the statements for you:
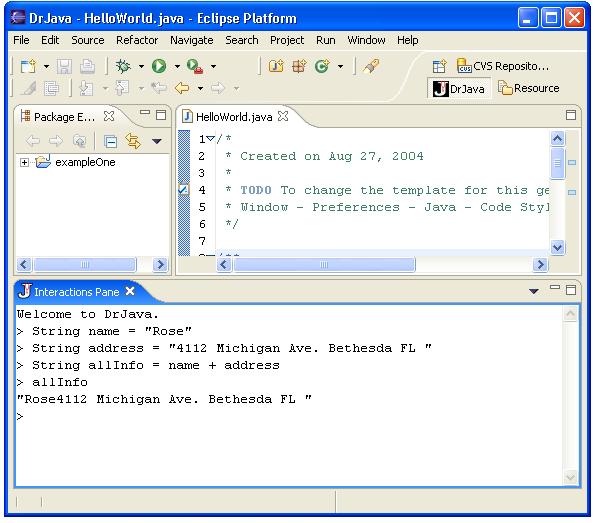
In addition to creating standard
Java objects, you can also create instances of objects you've defined in your
project. For example, let's say your project has a Foo class. After you
compile your project, you can type Foo f = new Foo() in the
interactions pane and experiment with your own code.
Sometimes, after you've declared
a bunch of variables and played with them, you may want to reset the
interactions pane so you can start from scratch. To do this, all you need to do
is right click anywhere in the interactions pane and click "Reset Interactions",
and you'll be given a fresh environment without any variables declared.
|
