4. The GIMP PDB
A D V E R T I S E M E N T
Before going into the details of the Perl-Fu script, we will describe how to
access the various the functionality of GIMP. All functions known to GIMP
are available through the procedural database (PDB). All the PDB functions
may be called from perl, as will be seen below. These PDB functions are
either internal to gimp, or have been made available through a plug-in or a
script extension, but as far as the caller is concerned there is no
difference. As we will see below, when a perl function is registered through
the register function, it will appear in the PDB as well.
Gimp/perl comes with a PDB browser available in Xtns>PDB Explorer.
(There is another PDB browser available in Xtns>DB Browser but the
PDB Explorer is more suited for Perl users.) This browser provides a way of
seeing all the functions in the PDB, as well as their input and output
parameters. E.g. the PDB Explorer entry for gimp_image_new, which
will be used in the example below looks like this:
| Name: |
gimp_image_new |
| Blurb: |
Creates a new Image with the
specified with, height, and type |
| In: |
INT32 |
width |
The width of the image |
| |
INT32 |
height |
The height of the image |
| |
INT32 |
type |
The type of image { RGB (0), GRAY (1),
INDEXED (2) |
| Out: |
| |
IMAGE |
image |
The ID of the newly created image |
| Help: |
Creates a new image, undisplayed with the
specified extents and type. A layer should be created and
added before this image is displayed, or subsequent calls to
'gimp_display_new' with this image as an argument will fail.
Layers can be created using the 'gimp_layer_new' commands.
They can be added to an image using the 'gimp_image_add_layer'
command |
|
All the the constants mentioned in the PDB Explorer have been defined within
Gimp::Fu and may be used within perl. E.g. I.e. a call to create a new image
of size 100x150 of type RGB looks as follows:
$img = gimp_image_new(100, 150, RGB)
The PDB entry above shows that gimp_image_new is called with three
parameters width, height, type. These are all of type INT32. This type and
other types will be explained below.
Script-Fu scripts are called just like any other script according to the
PDB signature in the PDB browser. E.g. to run the Script Fu basic one logo
just do:
script_fu_basic1_logo("Hello", 72,
"-*-utopia-*-r-*-*-72-*-*-*-*-*-*-*",
[0,0,0],[1,1,1]);
Unfortunately, as of the writing, calling Script Fu from perl has proved
a to make both ScriptFu and gimp very unstable and caused both of them to
crash. If any of the readers is able to describe what is needed to get it to
run successfully, I will happily include this in a future version of this
tutorial.
Note!
When calling a PDB function from
Perl::Gimp that has an image and a drawable as the two first
arguments, only the drawable should be given as argument in the
calling sequence. |
4.1. Gimp::Fu and the register function
Gimp-Fu is perl's answer to Script-Fu. It provides a simplified method for
accepting parameters for a script through a Gtk interface, just like
script-fu, but as we shall see below, it has some additional bells and
whistles. The main function for a Gimp-Fu script is the register
function. This function declares the interface of the script to gimp. The
register function takes the following 10 parameters, that must all
be provided:
- The name of the function - a string. This is the name of the
function as it will be known in the PDB.
- A small description - a string
- A help text - a string
- The authors name - a string
- The copyright of the script - a string
- Creation date - a string
- Menu path - a string. The path has one of the two forms:
- "<Toolbox>/Xtns/Perl-Fu/Script Name"
- "<Image>/Perl-Fu/Script Name"
If form 1. is given, then the script is a standalone script that appears
in the menu hierarchy under Xtns/Perl-Fu and takes all its inputs
through the Gimp::Fu interface frame. If form 2. is given on the other
hand, then the script is tied to the image menu popped up through the
right hand button over any image. In this case Gimp::Fu will add as the
first two parameters to the script the image and the drawable active
when the script was invoked.
- The acceptable image types - a string. This list contains a list of
image types acceptable. This field is only used for scripts that are in
the "<Image>" hieararchy. Possible values are listed in the table below:
| value |
meaning |
| * |
Any images are accepted |
| RGB |
RGB images |
| RGBA |
RGB images with alpha
channels |
| GREY |
Grey level images |
- Parameters - A reference to an array of parameters. (A reference to
an array in perl is simply an array written within square brackets).
Each parameter in turn is a reference to an array containg the following
four or five values:
- The type of the parameter. The types recognized by Gimp::Fu and
their perl are given in the following table:
| Type |
Possible forms |
Comment |
PF_INT
PF_INT32
PF_INT16
PF_INT8
|
42 |
A number. PF_INT is a
synonym to PF_INT32. |
PF_VALUE
PF_FLOAT
|
3.141 |
A floating point number.
|
PF_TOGGLE
PF_BOOLEAN |
0
1 |
A boolean value.
|
PF_SLIDER
PF_SPINNER
|
An integer value through
a slider and a spinner interface. The range parameter should
be specified and is interpreted as minimum, maximum, and
step, e.g. [0,100,1]. |

|
| PF_FONT |
-*-blippo-*-*-*-*-24-*-*-*-*-*-*-* |
A font in X11 font
format. This interface launches a font browser.
|
| PF_STRING |
"A string" |
A string |
PF_COLOR
PF_COLOUR |
[255,127,0]
#ff7f00
|
A color may either be
expressed as a reference to an array of three components, or
as a hexadecimal triple, proceeded by the hash sign. |
| PF_TOGGLE |
0
1 |
A boolean toggle
|
| PF_IMAGE |
- |
An image
|
| PF_DRAWABLE |
- |
A drawable.
|
| PF_BRUSH |
 |
A brush
|
| PF_GRADIENT |
 |
A gradient
|
| PF_PATTERN |
 |
A pattern
|
- The name of the parameter - a string
- A help text for the parameter
- Default value for the parameter. This should be given in the
form listed in the table above.
- An array defining allowed range for the value. This is only
possible for PF_SLIDER and PF_SPINNER.
- A reference to an array of return types of the sub in the 11th
parameter.
- The sub to be called - a reference to a sub . This subroutine will
be called when the associated menu entry declared through the
Menu
path described above. When the sub is called it is passed as
arguments the list of parameters declared in field 9, declared above,
and in the case of a "<Image>..." script, the active image and layer as
first and second parameters.
A reference to a sub in perl may be declared in two ways. Either by
declaring a subroutine at a different place in the source file, e.g.
sub run and reference it by writing \&run. An alternative
way is to write it inline by simply writing:
sub { ($text, $color) = @_ ; ... }
The sub is expected not need to display a new image after it has created
it. Instead it is expected to return the new image or images that were
created in accordance with the return types declared in parameter 10 of
the register call described above. This behaviour has been
added in order to be able to call the sub noninteractively. More about
that behaviour below.
4.2. A commented script
The following Gimp::Fu script example shows the steps described in the
previous section. It registeres a script that takes two values, the size of
the image and a color, and then produces an image of the requested size with
the requested color. Quite useless, but is shows the importent steps of how
to register a script, how to create a new image, and how to access some PDB
functions.
|
uni |
1: #!/usr/local/bin/perl -w
2:
3: use Gimp ":auto";
4: use Gimp::Fu;
5:
6: sub img_uni {
7: my ($size, $color) = @_;
8:
9: # Create a new image
10: $img = gimp_image_new($size, $size, RGB);
11:
12: # Create a new layer
13: $layer = gimp_layer_new($img, $size, $size, RGB,
14: "Layer 1", 100, NORMAL_MODE);
15:
16: # add the layer to the image
17: gimp_image_add_layer($img, $layer, -1);
18:
19: # Set the background to the required color
20: gimp_palette_set_background($color);
21:
22: # Paint the layer
23: gimp_edit_fill($layer, BG_IMAGE_FILL);
24:
25: # Return the image
26: return $img;
27: }
28:
29: register
30: "img_uni", # fill in name
31: "Create a uniform image", # a small description
32: "A tutorial script", # a help text
33: "Dov Grobgeld", # Your name
34: "Dov Grobgeld (c)", # Your copyright
35: "1999-05-14", # Date
36: "<Toolbox>/Xtns/Perl-Fu/Tutorial/Img Uni", # menu path
37: "*", # Image types
38: [
39: [PF_INT, "size", "Img size", 100],
40: [PF_COLOR, "color", "Img color", [255,127,0]]
41: ],
42: \&img_uni;
43:
44: exit main();
|
Most of these commands are directly copied out the PDB.
This script shows the essential steps of producing a stand-alone script:
| line(s) |
Description |
| 10 |
Creating a new image. |
| 13-14 |
Creating one or more layers. |
| 17 |
Attaching the layer to the image. |
| 19-23 |
Do some painting operations in the layers. |
| 26 |
Return the image to the caller |
| 29-42 |
Registration of the extension |
To test the script, save it in the directory $HOME/.gimp-1.2/plug-ins.
It must then be made executable through the command:
chmod +x $HOME/.gimp-1.2/plug-ins/uni
Then start gimp. It is generally a good idea to test the syntax of the
script with perl -c before starting gimp. (A more official
way to add scripts is to use the gimptool --install-bin command).
Note: Due to a bug in gimp (verified for version 1.2) it is not
possible to add scripts once gimp is running. On the other hand, it is
possible to change a script which has already been registered, as long as
the parameters don't change.
The script is now accessible through the menu system through the Xtns
top menu:
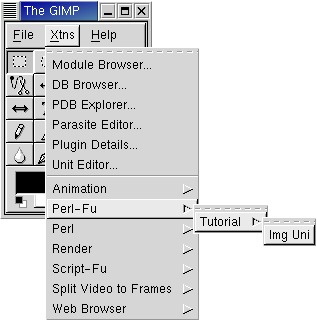
When choosing this menu entry the following screen is popped up:
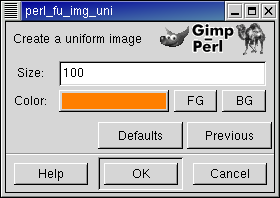
Choosing the default values result in the image:
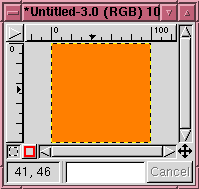
|
